
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) conducted its monetary policy meeting from February 6-8, 2024.
On the basis of an assessment of the evolving macroeconomic situation, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) made the following announcements:
These decisions are in consonance with the objective of achieving the medium term target for consumer price index (CPI) inflation of 4% within a band of +/- 2%, while supporting growth.
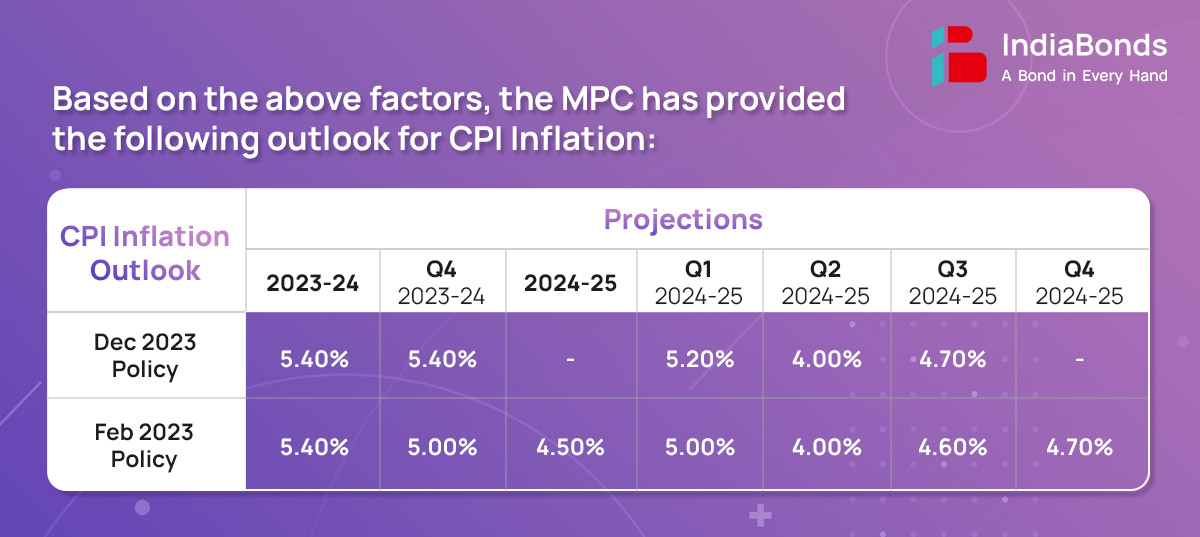
CPI Headline inflation moderated to an average of 5.5% during Apr’23-Dec’23 from 6.7% during FY22-23. Food price inflation, however, continued to impart considerable volatility to the inflation trajectory. In contrast, the deflation in CPI fuel deepened and core inflation moderated to a four-year low of 3.8% cent in Dec’23.
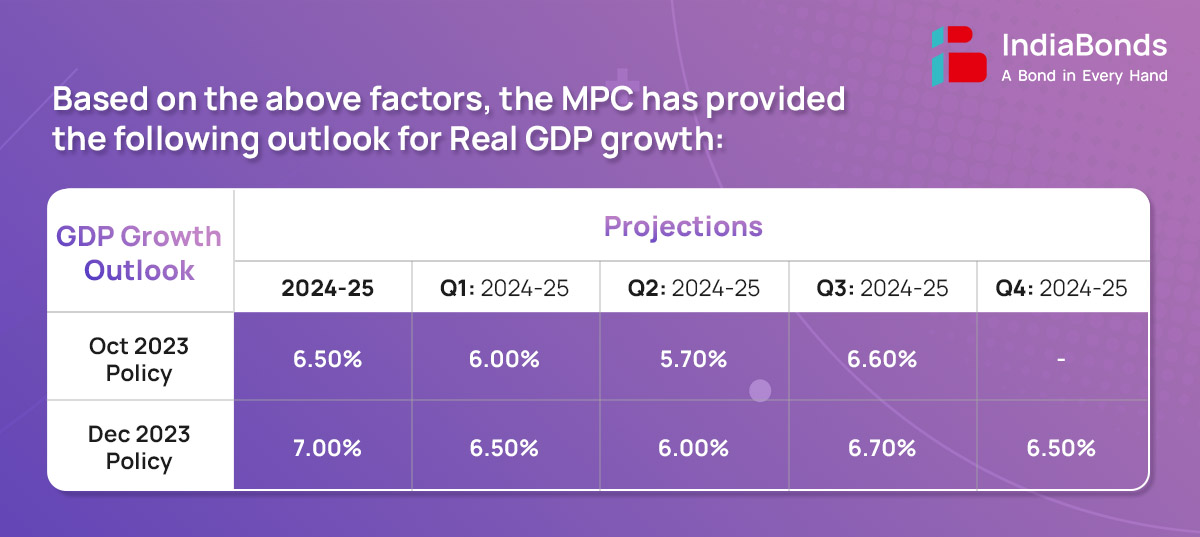
Domestic economic activity remains strong. The first advance estimates (FAE) placed the real gross domestic product (GDP) growth at 7.3% for 2023-24, marking the third successive year of growth above 7%.
Global growth is expected to remain steady in 2024 with heterogeneity across regions. Though global trade momentum remains weak, it is exhibiting signs of recovery and is likely to grow faster in 2024. Amidst the current headwinds, elevated level of public debt is raising serious concerns on macroeconomic stability in many countries, including some of the advanced economies (AEs).
Under the framework, which aimed to ensure fair access through transparent, safe, and efficient trading processes, robust trading infrastructures and prevent market abuse, 13 ETPs operated by 5 operators have since been authorized. In view of these developments, it has been decided to review the regulatory framework for ETPs. The revised regulatory framework will be issued separately for public feedback.
Resident entities can now hedge gold price risk in the over-the-counter (OTC) segment in the IFSC, in addition to recognised exchanges. This decision enhances flexibility and access to derivative products for hedging gold exposure. Instructions regarding this expansion are forthcoming, aiming to facilitate smoother operations for resident entities.
The RBI has mandated all regulated entities to provide a Key Fact Statement (KFS) to borrowers for all retail and MSME loans. This move aims to enhance transparency in loan pricing and empower borrowers with critical information such as the all-inclusive interest cost, aiding them in making informed decisions. The KFS requirement extends beyond scheduled commercial banks to encompass digital lending and microfinance sectors, ensuring consistency and clarity across the lending landscape.
AePS, managed by NPCI, facilitates digital payments for over 37 crore users, enhancing financial inclusion. To enhance security, the onboarding process for AePS touch point operators will be streamlined, with mandatory due diligence and enhanced fraud risk management.
The Reserve Bank aims to enhance digital payment security by adopting a principle-based framework for authentication, moving beyond SMS-based OTP. This shift aligns with emerging technological innovations in authentication methods. Specific instructions will follow separately.
The CBDC-R pilot plans to expand functionalities by enabling programmability for defined benefits and corporate expenditures. Additionally, offline functionality will be introduced to facilitate transactions in areas with poor internet connectivity. Various offline solutions will be tested across different locations.
The next meeting of the MPC is scheduled during April 3-5, 2024.
Disclaimer: Investments in debt securities/ municipal debt securities/ securitised debt instruments are subject to risks including delay and/ or default in payment. Read all the offer related documents carefully.