
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) conducted its monetary policy meeting from August 6-8, 2024. On the basis of an assessment of the evolving macroeconomic situation, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) made the following announcements:
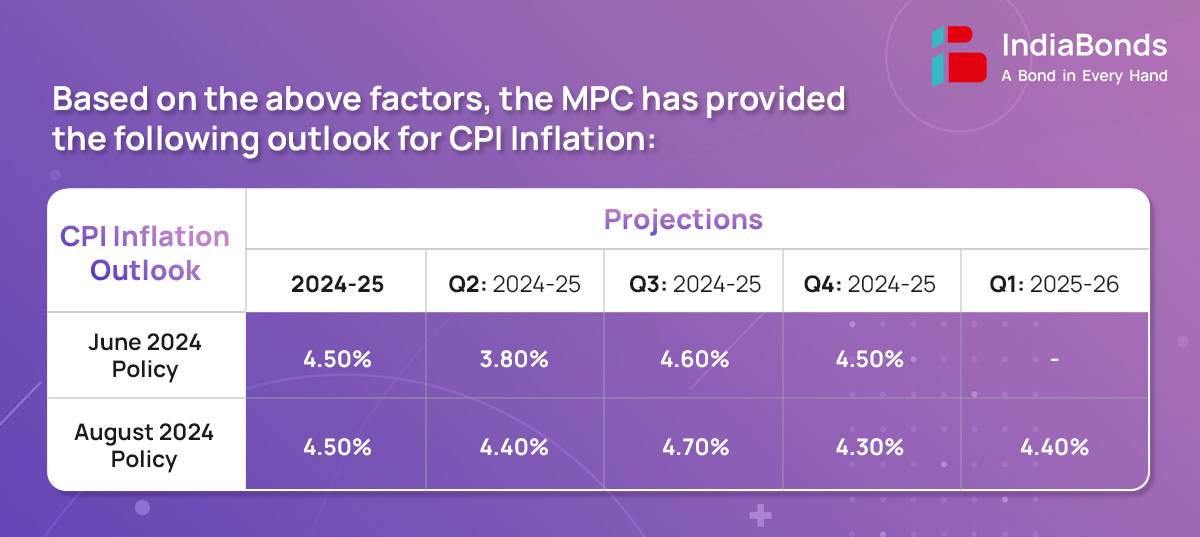
CPI headline inflation edged up in June after remaining steady during April – May, primarily driven by food components. Fuel prices remained in deflationary zone for the tenth consecutive month while core inflation continued to soften on broad based. Vegetable and edible oil prices experienced sharp increase, accompanied by rise in prices of cereals, milk, fruits and prepared meals primarily caused by supply side shock. Both core services inflation and core goods inflation witnessed slight slowdown in June.
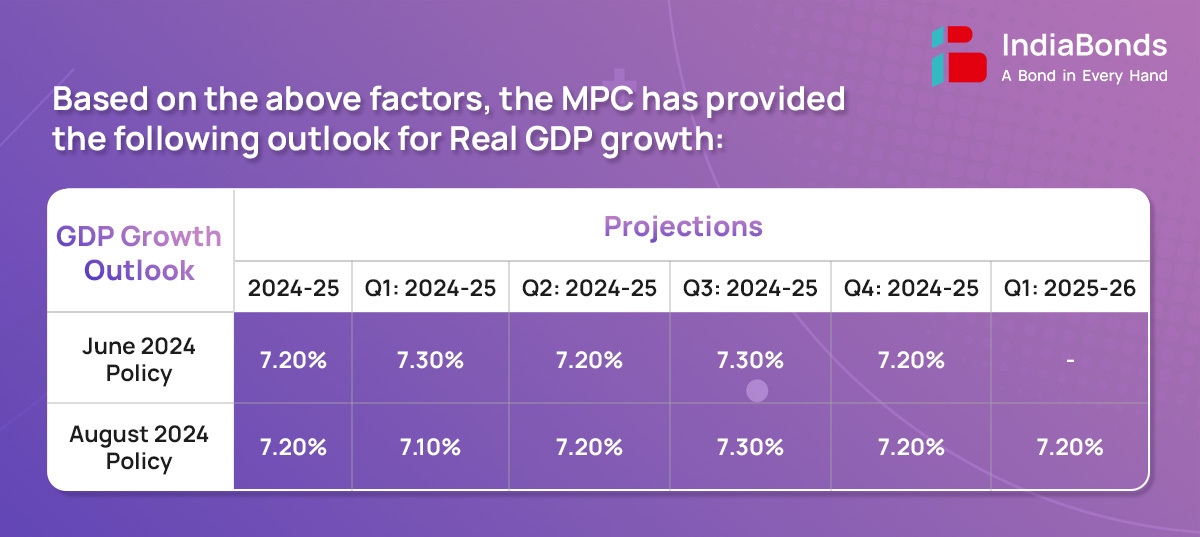
During 2024-25 so far, domestic economic activity has maintained resilience. Manufacturing activity continues to gain ground on the back of strengthening domestic demand. Private corporate investment is also gaining steam on the back of expansion in bank credit. The eight core industries posted growth of 4% in June 2024. Manufacturing PMI remained elevated while services PMI stood strong above 60 for seventh consecutive months, indicating robust expansion. Additionally merchandise and service exports hold high. Also the current account deficit moderated due to lower trade deficit and robust services and remittances receipts.
The global economy is expanding steadily but unevenly, with manufacturing slowing while services activity remains robust. Central banks across globe are cautiously adjusting their monetary policies, with some easing restrictions and others maintain tightening. Financial markets are volatile, with bond yields and the dollar index weakening recently. While short-term prospects appear optimistic, the global economy faces substantial challenges in the medium term.
RBI has proposed to launch a public repository that will list all Digital Lending Apps (DLAs) affiliated with Regulated Entities (REs), based on data submitted directly by REs. This repository will be updated regularly to reflect new additions or deletions.
The RBI has directed credit institutions (CIs) to report borrowers’ credit information to credit information companies (CICs) every fortnight, replacing the previous monthly reporting schedule. This updated frequency will enhance the overall effectiveness of credit assessment and risk management.
The RBI has decided to increase the UPI transaction limit for tax payments from Rs.1 lakh to Rs.5 lakh. UPI, a widely-used payment method, previously had a cap of Rs.1 lakh, though limits have been periodically reviewed and increased for various categories like capital markets, IPO subscriptions, and loan collections.
The RBI plans to introduce a new feature called “Delegated Payments” in UPI to enhance its utility. Delegated Payments will enable a primary user to set a UPI transaction limit for a secondary user on the primary user’s bank account.
The RBI plans to enhance the efficiency of the Cheque Truncation System (CTS) by transitioning from batch processing to continuous clearing with ‘on-realization-settlement’. Currently, CTS processes cheques with a clearing cycle of up to two working days. The new approach will enable cheques to be scanned, presented, and cleared within a few hours during business hours, reducing the clearing cycle from T+1 days to just hours.
The next meeting of the MPC is scheduled during October 7 to 9, 2024.
Disclaimer: Investments in debt securities/ municipal debt securities/ securitised debt instruments are subject to risks including delay and/ or default in payment. Read all the offer related documents carefully.