Union Budget FY2024-25

Fiscal Deficit
In the Union Budget of 2024-25, the government has revised India’s fiscal deficit target downward to 4.9% of GDP for FY24-25 from the previously estimated 5.1% of GDP in the interim budget. Fiscal deficit for FY23-24 stood at 5.6% of GDP, much lower than the FY23-24 budgeted estimates of 5.9% of GDP. In absolute terms, the government estimates fiscal deficit to decrease from Rs. 16.54 lakh crore FY24 PA to Rs. 16.13 lakh crore in FY25 BE.
The details of the revenues, expenditures and fiscal deficit are provided in the table below:
| Deficit Statistics | ||||
| 2023-24 BE | 2023-24 RE | 2023-24 PA | 2024-25 BE | |
| Fiscal Deficit | 17.87 | 17.35 | 16.54 | 16.13 |
| (5.9%) | (5.8%) | (5.6%) | (4.9%) | |
| Revenue Deficit | 8.70 | 8.41 | 7.66 | 5.80 |
| (2.9%) | (2.8%) | (2.6%) | (1.8%) | |
| Revenue Receipts | 26.32 | 27.00 | 27.28 | 31.29 |
| Revenue Expenditure | 35.02 | 35.40 | 34.94 | 37.09 |
| Capital Receipts | 18.71 | 17.91 | 17.14 | 16.91 |
| Capital Expenditure | 10.01 | 9.50 | 9.49 | 11.11 |
Budget Estimates 2024-25
- Total expenditure is estimated at Rs. 48.21 lakh crore in FY24-25, compared to Rs. 44.43 lakh crore in FY23-24. Of this, capital expenditure remains unchanged as estimated in Interim budget at Rs. 11.11 lakh crore, higher than the Rs. 9.49 lakh crore spent in FY23-24.
- Revenue expenditure is estimated at Rs. 37.09 lakh crore in FY24-25, compared to Rs. 34.94 lakh crore in FY23-24.
- Total tax revenue for FY24-25 is estimated at Rs. 25.83 lakh crore, higher than total tax revenue of Rs. 23.27 lakh crore in FY23-24.
- Non-tax revenue for FY24-25 is estimated to be higher at Rs. 5.46 lakh crore, compared to Rs. 4.02 lakh crore in FY23-24.
The Path to Fiscal Consolidation
- The government reinforced its commitment to the path of fiscal consolidation, to reach a fiscal deficit of 4.5% by 2025-26:
| Financial Year | 2023-24 BE | 2023-24 IB | 2023-24 PA | 2024-25 BE | FY’26 BE |
| Fiscal Deficit % of GDP | 5.9 | 5.8 | 5.6 | 4.9 | 4.5 |
Market Borrowings
- Gross market borrowings of the central govt. is estimated at Rs. 14.01 lakh for FY24-25, lower than interim budget estimate of Rs. 14.13 lakh crore.
- Net market borrowing for FY24-25 is estimated at Rs. 11.63 lakh crore, lower than interim budget estimate of Rs. 11.75 lakh crore.
- The balance financing of fiscal deficit is expected to come from small savings and other sources.
| Financial Year | FY’24 RE | FY’24 PA | FY’25 IB | FY’25 BE |
| Net Market Borrowing | 11.80 | 11.78 | 11.75 | 11.63 |
Impact on Bond Yields:
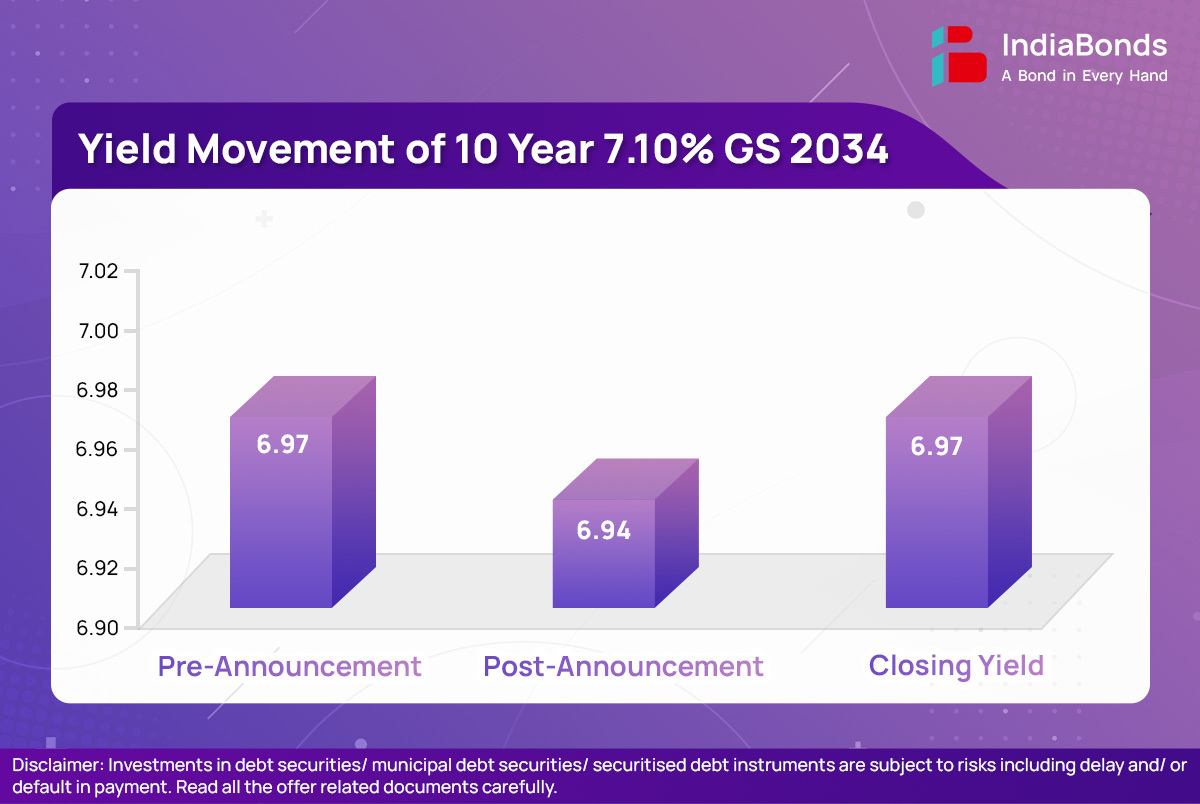
- The 10-year benchmark paper (7.10% GS 2034) rallied 4 bps to 6.93% from 6.97% after the announcement of deficit and borrowing numbers. However, this gain was reversed after the announcement of net market borrowing figures.
- The central’s net borrowing amount decreased marginally by Rs. 12,000 crore to Rs. 11.63 lakh crore against Rs. 11.75 lakh crore estimated in Interim Budget, and lower than market estimated decrease of Rs. 50,000 crore.
- Going forward, the bond market yields will be guided by the RBI’s upcoming monetary policy on 8th Aug 2024 and foreign fund inflows.
Capital Expenditure:
- The Budget stated that the government endeavors to maintain strong fiscal support for infrastructure. The centre aims to spend Rs. 11.11 lakh crore on capital expenditure in FY24-25, banking on its significant multiplier impact on economic growth and employment creation.
- Actual capital expenditure stood at Rs. 7.40 lakh crore in FY22-23 and Rs. 9.49 lakh crore in FY23-24.
- The central government will encourage states to provide similar scale of support for infrastructure and a provision of Rs 1.5 lakh crore for long-term interest free loans has been made to support the states in their resource allocation.
- Investment in infrastructure by private sector will be promoted through viability gap funding and enabling policies and regulations. A market-based financing framework will be brought out.
- Funds worth Rs. 2.66 lakh crore is being set aside for rural development including rural infrastructure.
Announcements on Taxation
Simplification and Rationalization of Capital Gains
| Classification of Long Term Capital Gains | |
| Assets | Duration |
| Specified Financial Assets | Above 1 Year |
| Other Financial Assets and all Non-Financials Assets | 2 Years & above |
| Rationalization of Capital Gains Tax | ||
| Short Term Capital Gains (STCG) | Certain Financial assets (Primarily Equity) | 20.00% |
| Other Financial assets and all non-Financial Assets | Applicable Tax rate | |
| Long Term Capital Gains (LTCG) | All Financial assets and all Non-Financial Assets | 12.50% |
| Unlisted bonds and debentures, debt mutual funds and market linked debentures, irrespective of holding period | Applicable Tax rate | |
Other Announcements
- Abolished Angel tax for all classes of investors to bolster the Indian start-up eco system
- Corporate tax rate reduced for foreign companies from 40% to 35%.
- STT on futures increased from 0.0125% to 0.02% while STT on sale of options increased from 0.0625% to 0.1% of the premium.
- 20% TDS on repurchase of units by mutual funds or UTI is being withdrawn.
- TDS rate on e-commerce operators reduced from 1% to 0.1%.
Personal Income Tax
- The standard deduction for salaried employees increased from Rs.50,000 to Rs.75,000.
- A non-government employee in the new tax regime shall be allowed deduction of an amount not exceeding 14% of the employee’s salary in place of 10%.
- Deduction of expenditure by employers towards NPS is increased from 10% to 14% of the employee’s salary.
- In the new tax regime, the tax rate structure is revised, as follows:
| Tax rate Structure (New Regime) | |
| Slab rate | Tax rate |
| 0-3 lakh rupees | Nil |
| 3-7 lakh rupees | 5.00% |
| 7-10 lakh rupees | 10.00% |
| 10-12 lakh rupees | 15.00% |
| 12-15 lakh rupees | 20.00% |
| Above 15 lakh rupees | 30.00% |
Customs Duty changes
- Reduction in custom duty on Gold bar and Silver bar from 15% to 6%.
- Reduction in custom duty of all critical minerals, Cancer drugs, textile, leather, steel, copper, capital goods, IT and electronics, medical equipment.
The following 9 priorities have been emphasized in the budget:
The budget proposes a roadmap for development primarily focusing on manufacturing to generate employment and promote upskilling. It also targets increasing agricultural productivity for food security, directing urban development, and fostering innovation and next-generation reforms.
1. Productivity and resilience in Agriculture
- A budget of Rs. 1.52 lakh crore is allocated for agriculture and allied sectors.
- The Agriculture Research Setup increase productivity and develop climate resilient varieties with funding through challenge mode, including for the private sector.
- Over the next two years, 1 crore farmers will be introduced to natural farming to achieve self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseeds.
- A digital public infrastructure in agriculture will cover farmers and their lands within 3 years, starting with a digital crop survey in 400 districts.
2. Employment & Skilling
- ‘Employment Linked Incentive’ with 3 new schemes.
- Scheme A provides one-month wages for new employees in formal sectors.
- Scheme B supports job creation in manufacturing by incentivizing EPFO contributions.
- Scheme C incentivizes employers with up to Rs. 3,000 per month for EPFO contributions for each additional employee.
- A skilling programme collaborates with state governments and industry to skill 20 lakh youth over 5 years.
- The Model Skill Loan Scheme offers loans up to Rs. 7.5 lakh with government guarantee, benefiting 25,000 students annually. Additionally, financial support for education loans up to Rs. 10 lakh with 3% interest subvention will be provided to 1 lakh students yearly.
3. Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
- Support for economic activities will be increased for artisans, self-help groups, scheduled castes, tribes, women entrepreneurs, and street vendors.
- The development of the Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor, with a node at Gaya, will boost industrial growth in the Eastern Region.
- Road projects costing Rs. 26,000 crore, as well as power projects like a new 2400 MW plant at Pirpainti costing Rs. 21,400 crore, will be initiated.
- Additional funding for capital investments and fast-tracking external assistance for Bihar and financial support for Andhra Pradesh will be provided for infrastructure development and economic growth.
- PM Awas Yojana to build 3 crore houses in rural and urban areas.
- Over Rs. 3 lakh crore allocated in budget for women-led development, enhancing women’s role in economy.
- India Post Payment Bank to open 100+ branches in North East;
- Rs. 2.66 lakh crore allocated for rural development this year.
4. Manufacturing & Services
- Credit guarantee scheme for MSMEs offering coverage up to Rs.100 crore per applicant.
- The Mudra loans limit has been enhanced to Rs.20 lakh from the current limit of Rs.10 lakh.
- The turnover threshold for mandatory onboarding of buyers onto the TReDS platform will be reduced from Rs.500 crore to Rs.250 crore, expanding access for 22 additional CPSEs and 7,000 more companies.
- New SIDBI branches in MSME clusters, opening 24 branches this fiscal year, with plans to cover 168 out of 242 major MSME clusters within 3 years
- Financial support to MSME Units for Food Irradiation, Quality & Safety Testing, facilitating 50 multiproduct food irradiation units and 100 food quality and safety testing labs with NABL accreditation.
- Internship opportunities to 1 crore youth in top 500 companies in 5 years. Also, allowance of Rs.5,000 per month along with a one-time assistance of Rs.6,000 through the CSR funds to be provided.
- The government aims to establish “plug and play” industrial parks in 100 cities and develop 12 industrial parks under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme to bolster industrial infrastructure.
5. Urban Development
- Transit Oriented Development plans for 14 large cities with a population above 30 lakh will be formulated.
- Invest Rs.10 lakh crore to provide housing for 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families, with Rs.2.2 lakh crore allocated for central assistance over 5 years.
- Promote water supply, sewage treatment and solid waste management projects and services for 100 large cities through bankable projects.
6. Energy Security
- Under PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana the Govt. aims to install rooftop solar plants providing free electricity up to 300 units monthly to 1 crore households.
- Research and development of small and modular nuclear reactor expected to form a very significant part of the energy mix.
- Indigenous AUSC technology for thermal power plants has led to an 800 MW commercial plant by NTPC and BHEL
- Investment-grade energy audits for micro and small industries in 60 clusters, enabling transition to cleaner energy and efficiency measures, with plans to extend to 100 more clusters.
7. Infrastructure
- A provision of Rs.11.11 lakh crore is made for infrastructure (which is 3.4% of GDP).
- Investment in infrastructure by private sector will be promoted through viability gap funding
- Launch 12 industrial parks under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme as well as phase IV of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) for providing all weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations.
- A joint venture between NTPC and BHEL to set up a full scale 800 MW commercial plant- AUSC Thermal Power Plants.
- More than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank will be set up in the North East region.
- For irrigation and flood mitigation purpose a financial support of Rs.11500 is allocated for various projects such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 other ongoing and new schemes.
- A sum of Rs.26000 crore is allocated for road connectivity projects and another sum of Rs.21400 crore will be used for power projects including setting up of a new 2400 MW power plant at Pirpainti.
- Development of Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor along with development of an industrial node at Gaya.
- Essential infrastructure such as water, power, railways and roads are proposed to construct in Kopparthy node on the Vishakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor and Orvakal node on Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
8. Innovation, Research & Development
- Operationalization of the Anusandhan National Research Fund for fostering culture of research and prototype development.
- Encouraging private sector in innovation and R&D through a allocated pool of Rs.1 lakh crore
- Government in partnership with private sector is working on R&D of Bharat Small Modular Reactor and new technologies for nuclear energy.
- To boost space economy by 5 times in the next 10 years, a venture capital fund of Rs.1,000 is set up.
- With Agricultural research center focusing on high productive and climate-resilient crops, new 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops will be released.
- Additionally 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres will be establish for aiding natural farming.
9. Next Generation Reforms
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands, digitization of cadastral maps, establishment of land registry so as to facilitate credit flow and other services in rural area
- For urban areas, digitalization of land records, with GIS mapping for property records and tax administration.
- Focus on building a taxonomy for climate finance to enhance availability of capital and to achieve nation’s climate commitments and green transition.
- Emphasis on easing rules and regulations for FDI and Overseas Investments as well as promoting opportunities for using Indian Rupee as a currency for overseas investments.
- Another initiative, NPS-Vatsalya aims to enable parents and guardians to contribute to minors until they achieve maturity.
Key Takeaways from the budget:
Aggressive Fiscal Consolidation
The market expected the fiscal deficit to be maintained at the most at 5.1% in view of the need to have a populist budget considering coalition compulsions. However, the FM announced a significant lower number at 4.9% of GDP. The improvement of 20 basis points over interim budget, primarily due to a higher than expected dividend transfer from the RBI , exceeded mar ket expectations. This also reinforced the government’s commitment to achieving a fiscal deficit target of 4.5% by FY25-26.
Simplification of the Tax Structure
The Capital Gain Tax Structure has been now simplified to broadly 2 tenures (1 Year and 2 Year) and 2 rates (Specified financial assets and other financial & non-financial assets). The standardization of tax rate on capital gain both short term and longterm is expected to help in rationalisation and simplification of tax structure. The increase of exemption limit of capital gains on certain financial assets from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 1.25 lakh will benefit lower and middle-income classes. Also, increased STT of derivative products such as options and futures may discourage speculative derivative trading.
Focus on Job Creation
There has been criticism over the government’s performance in the area of employment generation. The budget has tried to address it through slew of announcements in this area. The budget announced a package of 5 schemes and various other initiatives. The package aims to facilitate employment, skilling, and other opportunities for 4.1 crore youth over a 5-year period with a central outlay of Rs. 2 lakh crores. Additionally, employmentlinked incentives for both employers and employees will likely address concerns surrounding employment and job creation.
Addressing Rural Sector Distress
The rural sector has been under stress, with subdued wage growth and higher food inflation levels. The targeted spending of Rs. 2.66 lakh crores for rural development, including rural infrastructure, along with the provision of Rs. 1.52 lakh crores for agriculture and allied sectors, will likely boost economic activities in rural areas and create avenues for rural employment.
Continued focus on Infrastructure
The proposed capital expenditure of Rs. 11.11 lakh crore indicated continuation of its focus on Infrastructure sector. Considering the need to cater to the various areas namely agriculture, employment, and subsidies to various groups and pandering to allies demand, the budget has managed to balance the Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure within the budget.
Managing politically important alliance states of the coalition
The budget tried to accommodate the demands of its coalition partners through special announcement of financial assistance, schemes and project to the states of Bihar and Andhra Pradesh. The announcement underscored the new political reality in the third term of the government.
Disclaimer: Investments in debt securities/ municipal debt securities/ securitised debt instruments are subject to risks including delay and/ or default in payment. Read all the offer related documents carefully.














































