April’ 2025 Monetary Policy Highlights and Rationale

The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) conducted its monetary policy meeting from April 7-9, 2025.
On the basis of an assessment of the evolving macroeconomic situation, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) made the following announcements:
- Reduced the policy repo rate by 25 bps from 6.25% to 6.00% unanimously, consequently the standing deposit facility (SDF) is reduced to 5.75%.
- Accordingly, the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate and the Bank Rate changed to 6.50%.
- The reverse repo rate under the LAF stands unchanged at 3.35%.
- The MPC also decided unanimously to change the stance from ‘neutral’ to ‘accommodative’ and remain unambiguously focused on a durable alignment of inflation with the target, while supporting growth.
Part A: RBI’s Policy decision Rationale:
1. Inflation
CPI Headline inflation eased sequentially in Feb’25 and Jan’25 from its recent peak of 5.2% in Dec’24. The decline was primarily driven by a moderation in food inflation, as vegetable price inflation retreated from its Oct’24 high. Core inflation, which had held steady between Dec’24 and Jan’25, edged upwards to 4.1% in Feb’25. This increase was primarily driven by a notable rise in the price of gold.
The MPC expects CPI outlook to be shaped by several factors such as:
- Improved rabi crop prospects (record wheat, higher pulses), and strong kharif arrivals are expected to lead to a durable softening of food inflation.
- Declining inflation expectations and falling crude oil prices offer a positive outlook, but lingering global market uncertainties and potential weather-related supply disruptions pose risks to higher inflation.
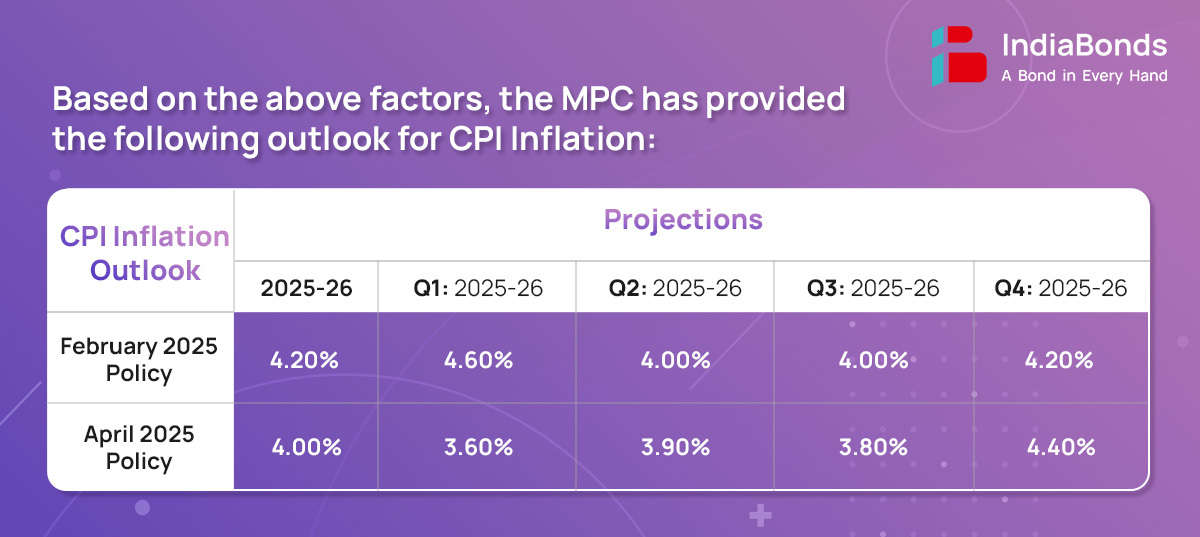
- Assuming a normal monsoon, CPI inflation is projected at 4.0% for the current fiscal year. For FY25-26 CPI is expected at 4.0% with Q1 at 3.6%, Q2 at 3.9%, Q3 at 3.8% and Q4 at 4.4%.
2. Growth
Strong agricultural prospects, a recovering manufacturing sector, and resilient services are expected to drive robust domestic demand and increasing investment in 2025-26. While services exports should remain strong, merchandise exports face global headwinds and trade risks. Going forward, sustained rural demand, anticipated urban consumption revival, and expected fixed capital formation recovery backed by government spending, capacity use, and healthy balance sheets are projected to support future growth.
The MPC expects real GDP to be based on the following factors:
- Bright prospects of the agriculture sector bode well for rural demand which continues to be healthy. Urban consumption is gradually picking up with an uptick in discretionary spending.
- Investment activity is expected to improve further on the back of sustained higher capacity utilization, government’s continued thrust on infrastructure spending.
- Healthy balance sheets of banks and corporates, along with the easing of financial conditions. Merchandise exports will be weighed down by global uncertainties, while services exports are expected to remain resilient.
- Headwinds from global trade disruptions continue to pose downward risks.
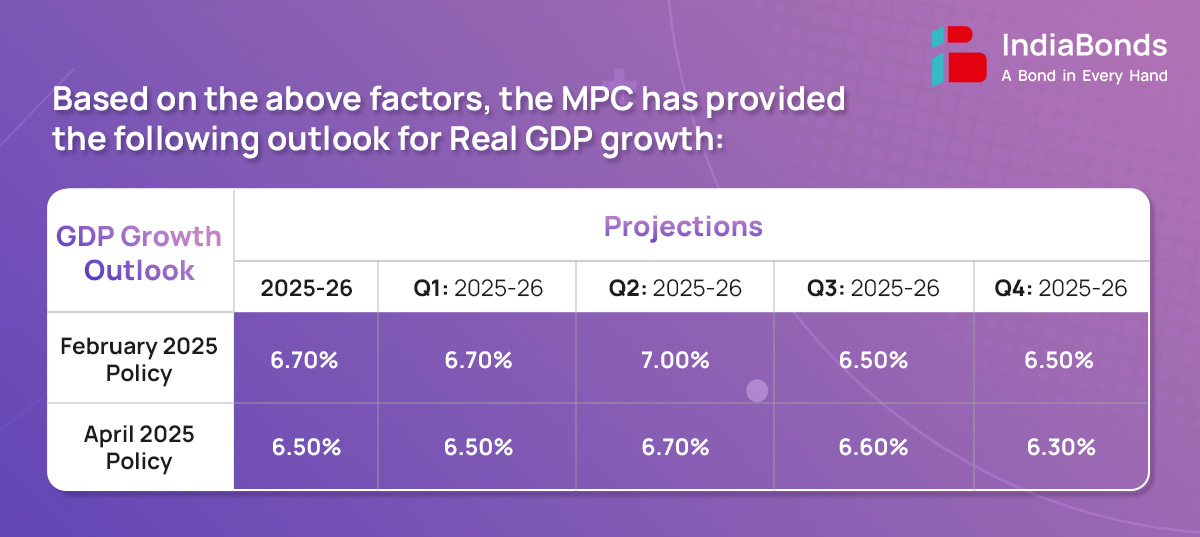
- Taking all these factors into account, real GDP growth for FY25-26 is projected at 6.50%, with Q1 at 6.50%, Q2 at 6.70%, Q3 at 6.60% and Q4 at 6.30%.
3. Liquidity
- System liquidity moved from a deficit peaking at Rs. 3.1 lakh crore on January 23, 2025, to a surplus of Rs. 1.5 lakh crore by April 7, 2025, following Rs. 6.9 lakh crore in liquidity injections and increased government spending.
- RBI infused nearly Rs. 7 lakh crore into the banking system through a host of measures including bond purchases Open Market Operations, forex swaps, and variable rate repo auctions up to early April 2025.
- Following recent developments, the weighted average call rate softened and stayed close to the repo rate, indicating improved liquidity conditions.
- Going forward, RBI will continue to be proactively taking appropriate measures to ensure orderly liquidity conditions.
Global Economy
The rapidly evolving global economic outlook is increasingly uncertain due to recent trade tariff measures, creating headwinds for global growth and inflation. This turbulence has led to a weaker US dollar, softer bond yields, equity market corrections, and crude oil prices at a three-year low. Central banks are responding cautiously, exhibiting policy divergence based on their domestic priorities. The Indian economy is steadily progressing towards price stability and sustained growth, while remaining vigilant against global uncertainties and weather disturbances.
Part B: Key Statements on Developmental and Regulatory Policies:
1. Market-Based Securitisation of Stressed Assets
RBI has proposed to introduce a market-based securitization framework for these assets. This initiative will complement the existing Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) route under the SARFAESI Act, providing an additional avenue for banks and other regulated entities to offload stressed exposures and improve their balance sheets.
2. Scope of Co-Lending Arrangements
The RBI will extend the current co-lending guidelines for priority sector lending to all regulated entities (REs). The revised framework will expand applicability beyond banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) to include all REs.
3. Standardizing Regulations for Gold Loans
To ensure consistency, transparency, and consumer protection in the widespread gold loan market, while
considering varying institutional risk capacities, the RBI intends to standardize prudential and conduct regulations for all regulated entities involved.
4. Guidelines for Non-Fund-Based Facilities and Enhancing Infrastructure Financing
To streamline regulations and foster uniformity across the financial sector, the RBI will issue comprehensive guidelines for non-fund-based facilities. Revisions to partial credit enhancement (PCE) aim to broaden funding for critical infrastructure projects and encourage greater financial institution participation, supporting economic development.
The next meeting of the MPC is scheduled during June 4 to 6, 2025.
Disclaimer: Investments in debt securities/ municipal debt securities/ securitized debt instruments are subject to risks including delay and/ or default in payment. Read all the offer related documents carefully.
















































